Key Takeaways
- Minecraft is not officially banned in any country. Most “bans” are indirect results of gaming laws, sanctions, or platform restrictions—not formal government prohibitions.
- Restrictions usually come from regulation or geopolitics, not the game itself. Youth protection laws, international sanctions, and internet governance policies shape access far more than concerns about Minecraft’s content.
- Access problems are often platform-based. App store removals, payment blocks, and disabled Microsoft services are the main reasons players lose access.
- Minecraft restrictions impact education, communities, and creators. Limits affect classroom learning, youth social networks, and a global creator economy.
- Most players can maintain access legally and securely. With proper tools and awareness, access to servers, updates, and marketplaces remains possible in most regions.
Minecraft is more than just a video game; it is a global cultural phenomenon. Since its official release in 2011, the “sandbox” title developed by Mojang Studios has sold over 300 million copies, making it the best-selling video game in history. Its open-ended nature allows players to build entire civilizations, learn complex coding through Redstone, and even recreate historical landmarks. Because of its “E for Everyone” rating and significant presence in classrooms through the “Education Edition,” Minecraft is generally perceived as the most “wholesome” corner of the internet.
However, the game’s freedom is exactly what has led it into the crosshairs of various governments. From investigations into “in-game violence” to geopolitical sanctions and strict national gaming regulations, the path of Steve and Alex has not always been smooth. While Minecraft is rarely subject to a “total permanent ban” in the way some social media platforms are, many countries have restricted, investigated, or partially blocked the game for reasons ranging from child safety to international diplomacy.
This guide explores which countries have banned or restricted Minecraft, the complex reasons behind these decisions, and how players can maintain access to their creative worlds.
Minecraft Restriction Status: Verified Overview by Country
Minecraft remains legally available in nearly all countries worldwide. However, in a small number of regions, players have experienced regulatory scrutiny, age-based restrictions, corporate service limitations, or content-specific access issues.
The table below reflects verified conditions only, based on publicly documented laws, official policy changes, and reliable reporting.
| Country | Restriction Type | Timeline | Current Status / Context |
| Turkey | No official restriction | N/A | Minecraft is fully legal and accessible. In 2015, Turkish authorities publicly discussed reviewing violent video games, but no investigation, ban, or regulatory action against Minecraft was ever implemented. |
| South Korea | General youth gaming regulation (non-Minecraft specific) | 2011 – 2021 | Minecraft was indirectly affected by South Korea’s former “Shutdown Law,” which restricted minors from playing online games late at night. The law applied broadly to online games, was not a Minecraft-specific ban, and was officially repealed in 2021. |
| Russia | No confirmed market withdrawal | 2022 – Present | While Microsoft suspended some business operations in Russia following international sanctions, there is no authoritative confirmation that Minecraft sales or updates were fully discontinued nationwide. Player access may vary by platform or payment method. |
| Iran | Corporate service limitations due to sanctions | Ongoing (variable) | Minecraft is not officially banned by the Iranian government. Some Iranian players report access or account issues, likely resulting from Microsoft’s compliance with U.S. sanctions rather than domestic censorship. No formal ban has been announced. |
| Vietnam | Content-specific or server-level interference | Periodic | Minecraft itself is not banned in Vietnam. Occasional access issues reported by players typically involve specific servers or politically sensitive content (e.g., custom worlds), not the core game or official servers. |
Why Do Countries Restrict or Ban Minecraft? (Reason Analysis)
Controversy around Minecraft rarely stems from its core gameplay or graphics. Instead, issues arise where the game intersects with national regulations, online freedom conditions, or public policy goals such as youth protection and content control. The following points explain why and how this happens in some countries, supported by authoritative data.
1. Gaming Curfews and Youth Protection Laws
South Korea: Shutdown/Cinderella Law
South Korea implemented a national policy known as the “Shutdown Law” in 2011, which prevented children under 16 from playing online games between 00:00 and 06:00 as part of efforts to reduce gaming addiction and promote healthy sleep. This policy affected many online titles, including Minecraft, because enforcing age verification on online gameplay was legally required.
Outcome:
- The law was formally abolished in August 2021, ending mandatory curfews on minors playing online video games.
- After 2021, South Korea shifted toward a “Gaming Time Selection System” that allows parental control without a blanket midnight ban.
This illustrates how broad public policy on youth gaming addiction—even if not Minecraft-specific—can indirectly affect how game publishers (like Microsoft) adapt age verification and access controls.
2. Internet Freedom & Content Controls
Minecraft and other online platforms sometimes fall into a larger ecosystem of internet governance and content control. According to Freedom House’s Freedom on the Net 2025 report:
- Global internet freedom has declined for 15 consecutive years, driven by government efforts to control online information and expression.
- Censorship and other digital controls are being used increasingly to regulate who can access certain services or share content online, which is relevant when governments block servers or digital platforms.
What This Means for Games: Measures aimed at controlling online expression and digital platforms—whether to counter political content or to enforce age/identity verification—can influence game availability, connectivity, and ancillary services even if the game itself isn’t legally banned.
3. Statistics on Public Awareness of Age Restriction Laws
Survey Data on Awareness of Gaming Curfews
While Minecraft itself is not banned in these contexts, the presence of youth gaming laws has shaped public perception and regulatory debate:
As of 2024, survey data show that the Shutdown Law in South Korea (which forbade children under 16 from playing online video games between midnight and 6 a.m.) is broadly known among gamers, highlighting how regulatory frameworks influence youth gaming norms even after policy repeal.
This reflects that public knowledge of regulation can be a factor in how games are marketed, how age verification is implemented, and how controversies (like Minecraft’s age gating) gain traction.
4. Age & Content Rating Frameworks
Global Rating Systems

Although tools like PEGI or local rating bodies are not directly listed from the specified sources, broader rating systems and national content classification schemes contextualize game restrictions:
Many countries have compulsory content rating systems that influence how video games (including Minecraft) are labeled and accessed. For example, South Korea’s classification for video content (including games) extends to age-specific labels such as 19+ for certain media.
These age ratings inform platform behavior (e.g., age gates on account creation), and they demonstrate how non-Minecraft-specific regulation still shapes gameplay experiences across jurisdictions.
The Impact of Minecraft Restrictions
When access to Minecraft is limited by regulation, corporate compliance, or server-level blocking, the consequences extend far beyond the disappearance of a recreational game. Minecraft today functions simultaneously as an educational platform, a social infrastructure, and a digital economy. Even partial restrictions therefore produce ripple effects that touch learning systems, youth communities, and creative industries.
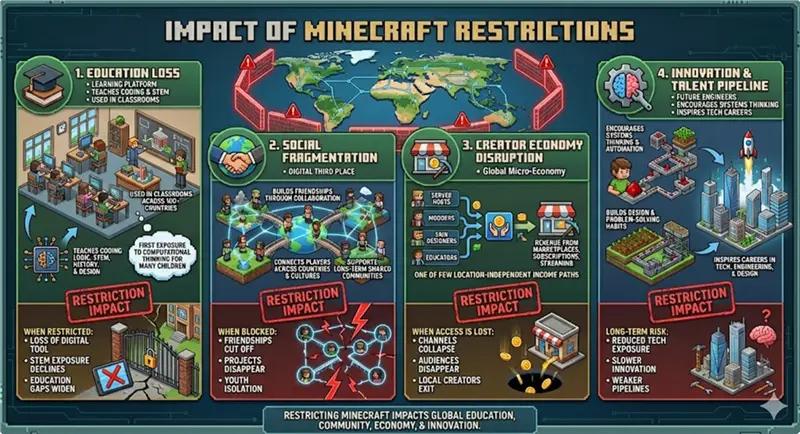
1. The Loss of Educational Infrastructure
Over the past decade, Minecraft has evolved into a formal learning environment through Minecraft: Education Edition, now adopted in classrooms across more than one hundred countries. Teachers use the platform to introduce students to programming logic, chemistry simulations, historical reconstructions, architectural design, and collaborative problem-solving.
For many children, Minecraft represents their first encounter with computational thinking. Redstone circuits, command blocks, and visual scripting provide an intuitive introduction to “if-then” logic long before formal coding courses appear in the curriculum.
When access becomes restricted, the impact is immediate. Schools lose a low-cost, high-engagement teaching platform, and carefully designed lesson plans must be abandoned. In regions where digital education tools are already scarce, these restrictions can widen the technology gap between students and slow early exposure to skills that increasingly define modern careers.
2. Social Isolation and Community Fragmentation
Beyond education, Minecraft functions as a digital “third place” for millions of young players — a shared social environment distinct from home and school where friendships form through collaboration rather than competition.
Communities are built through persistent worlds, long-term cooperative projects, and international servers that bring together players across languages and cultures. Unlike social media, relationships in Minecraft are created through shared construction and problem-solving.
When server access is blocked or platforms become unreachable, these social structures can collapse overnight. Cross-border friendships disappear, multi-year collaborative builds become inaccessible, and players are cut off from global peer networks. In regions with limited offline youth spaces, the loss of these communities removes one of the few creative and structured social outlets available to young people.
Over time, this fragmentation weakens cultural exchange, informal language learning, and the collaborative habits that digital communities naturally cultivate.
3. Economic Disruption for Creators and Micro-Entrepreneurs
Minecraft supports a decentralized global creator economy that extends far beyond the official game studio. Thousands of individuals earn income as server hosts, mod developers, skin designers, map architects, educators, and content creators on platforms such as YouTube and Twitch.
This ecosystem depends on access to:
- International audiences and servers
- Marketplaces and in-game monetization systems
- Advertising, subscriptions, and donation platforms
When access is restricted or markets become partially unavailable, creators lose not only players but also revenue infrastructure. Payment systems may fail, marketplaces become unreachable, and years of audience building can vanish instantly. For creators in sanctioned or restricted regions, this often means forced exit from the global digital economy, even when their work is educational and apolitical.
In many developing markets, Minecraft-related creation represents one of the few location-independent income paths available to young digital workers. Restrictions therefore, carry disproportionate economic consequences.
How to Access Minecraft Securely: Solutions & Legalities
If you are traveling to or residing in a region where Minecraft access is restricted—whether by local ISP blocks or developer-side sanctions—there are ways to reclaim your creative freedom safely.
1. Using a VPN for Minecraft
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is the most effective tool for bypassing regional restrictions. By encrypting your internet traffic and routing it through a server in a different country (such as the US, UK, or Germany), you can:
- Bypass IP blocks: Access servers like The Uncensored Library that may be blocked by local ISPs.
- Access Official Stores: Download updates and access the Minecraft Marketplace if the game has been removed from your local app store.
- Improve Connection Stability: In some cases, a VPN can help bypass “throttling” (where an ISP intentionally slows down gaming traffic).
2. Choosing the Right Tool: BearVPN
When gaming, not all VPNs are created equal. Speed and latency (ping) are the most critical factors. High latency leads to “lag,” making it impossible to play in competitive modes or survive in a treacherous survival world.
BearVPN is a recommended solution for Minecraft players because:
- Low Latency Servers: It offers high-speed servers optimized for gaming, ensuring that your blocks place instantly and your character doesn’t lag during combat.
- Global Server Network: With 2000+ servers across the globe, you can easily switch your virtual location to a region where Minecraft is fully supported.
- Security & Privacy: It uses advanced encryption to protect your account details from hackers on public Wi-Fi or unsecure networks.
3. Important Legal and Ethical Considerations
While using a VPN is legal in most countries, it is important to:
- Check Local Laws: Ensure that the use of VPN technology itself is not restricted in your current location.
- Respect the EULA: Always adhere to Mojang’s End User License Agreement. Avoid using a VPN to engage in “griefing” or breaking the rules of specific private servers.
- Avoid Illegal Downloads: Do not use restrictions as an excuse to download “cracked” or pirated versions of the game, as these often contain malware that can compromise your computer.
FAQ: Common Questions About Minecraft Bans
- Is Minecraft banned in Iran?
Technically, the Iranian government has not banned the game’s content. However, players in Iran are often blocked from accessing Microsoft and Xbox Live services due to international sanctions, making the game effectively unplayable without a VPN.
- Is Minecraft banned in Russia?
As of 2022, Microsoft has suspended the sale of Minecraft in Russia. While the game isn’t “illegal” to own, new players cannot buy it, and existing players face significant hurdles in receiving updates or accessing official multiplayer “Realms.”
- Why was Minecraft investigated in Turkey?
The investigation was triggered by concerns that the game’s survival mechanics—specifically killing mobs—promoted violence and social isolation in children. The government ultimately did not ban the game but issued warnings about its use.
- Is Minecraft “Adults Only” in South Korea?
Not anymore. While it was restricted to players 19 and older for a decade due to the “Cinderella Law,” those regulations were abolished in 2022. The game is now available to all age groups in South Korea.
- Can I get banned for using a VPN on a Minecraft server?
Most private servers allow VPNs. However, some very large “minigame” servers (like Hypixel) may temporarily block VPN IP addresses to prevent hackers from making “alt” accounts. Always check the specific server rules before connecting.
Conclusion
Minecraft remains a beacon of creativity, but its journey shows that even a sandbox made of blocks is not immune to the complexities of the real world. Whether it is a government’s concern over digital violence or the fallout of international diplomacy, access to the game can change overnight. By understanding these restrictions and using tools like BearVPN, players can ensure that their digital worlds remain open, no matter where they are on the map.