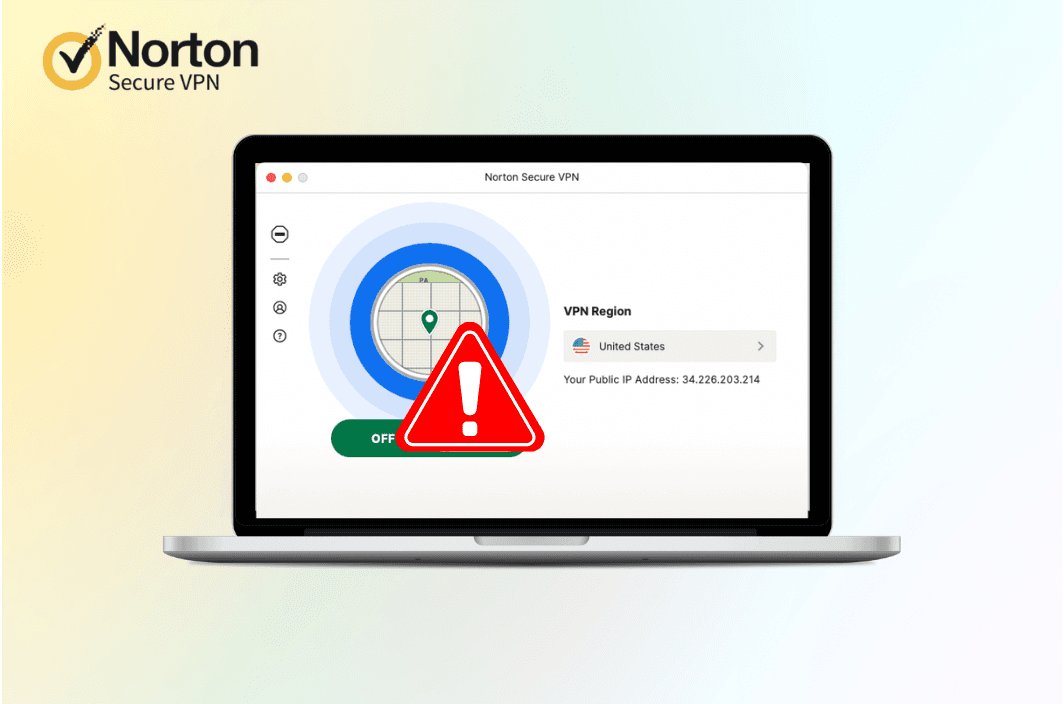
Norton Secure VPN, whether installed as part of Norton 360 or as a standalone application, is intended to encrypt internet traffic, protect private information, and maintain online security. However, many users encounter problems where Norton VPN stops working, fails to connect to its servers, or repeatedly disconnects. These issues can occur across Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS devices and often lead users to search quickly for solutions because a non-functioning VPN leaves online activity unprotected.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed breakdown of why Norton VPN may not work and how to fix the most common issues. The content follows a clear troubleshooting sequence to help ensure each potential cause is properly ruled out. Additionally, the article includes a balanced evaluation of Norton’s VPN stability and performance compared to alternatives such as BearVPN, which may offer a more reliable long-term solution if problems persist.
The primary objective is simple: get Norton VPN working again as efficiently as possible. If that cannot be achieved, the secondary objective is to ensure users can continue browsing securely by choosing a more dependable VPN option.
Why Norton VPN Stops Working
Norton Secure VPN relies on proper coordination between software, network services, permissions, and server connections. If any of these fail, the VPN tunnel cannot be established. Most issues are not caused by Norton alone but by how the device or network interacts with the VPN.
The most common causes include:
- Unstable or weak internet connectivity prevents the VPN from completing its secure handshake.
- Firewall restrictions from Norton Smart Firewall, Windows/macOS firewalls, or other security software that block encrypted traffic.
- Conflicts with other VPN or proxy services are still installed on the device, since only one tunneling service can operate at a time.
- Outdated versions of Norton VPN or the device operating system that introduce compatibility issues or software bugs.
- Overloaded or unavailable Norton VPN servers in the selected region, resulting in connection loops or slow performance.
- Account-related issues, such as expired subscriptions or device limits, prevent the VPN feature from activating.
Since multiple factors can contribute simultaneously, following a structured troubleshooting process is the most effective way to restore proper VPN functionality.
How to Fix Norton VPN Not Connecting (Step-by-Step)
The following solutions progress from the simplest checks to more advanced adjustments. After completing each step, try reconnecting the VPN before moving on.
1. Confirm Internet Connection Status
Turn off Norton VPN temporarily and test general internet access. If websites cannot load or the connection is unstable, restart the router, switch networks, or try mobile data. VPNs cannot operate without reliable connectivity.
2. Restart the Device and the Norton Application
Fully close Norton (including background services) and reboot the device.
This clears temporary software faults that can interrupt the VPN tunneling process.
3. Check Login and Subscription Status
Ensure you are logged into the correct Norton account and the subscription is active.
Use the “Subscription Status” refresh function if available. If the password was changed recently, login must be refreshed on all devices.
4. Update Norton Software and the Operating System
Install the latest version of Norton Secure VPN or Norton 360, then restart your device.
Updates often address compatibility issues — especially after system upgrades like Windows 11 or major iOS updates.
5. Change to Another VPN Server Location
Server issues may cause failure to connect.
Switch to a different region and try again to determine if the problem is server-related.
6. Modify VPN Protocol Settings
If supported in your version, change from automatic to another protocol (e.g., Norton’s Mimic mode).
This helps when networks block certain encryption methods, such as in workplaces or public Wi-Fi.
7. Adjust Firewall Permissions
Firewalls may restrict VPN traffic. Temporarily disable Norton Smart Firewall or the operating system firewall and reconnect.
If the VPN works, add Norton Secure VPN to the allowed list before re-enabling firewall protection.
8. Reset Network Configuration (Windows)
Issues with network adapters or TCP/IP settings can prevent secure tunneling.
Resetting the network stack and DNS clears corrupted routing data that could block connection attempts.
9. Reinstall Norton Secure VPN or Norton 360
If VPN components are damaged, removing and reinstalling the software restores critical files.
Restart once installation is complete and test VPN access again.
10. Contact Norton Support
If none of the above solutions work, provide error details to Norton Support.
They can check account validation issues, device authorization limits, or temporary server-side problems.
Most Norton VPN connection failures can be resolved by following these steps. In more complex cases, environmental network restrictions or software compatibility issues may require additional troubleshooting or consideration of alternative VPN services.
Device-Specific Norton VPN Troubleshooting
Norton VPN may behave differently depending on the operating system because each platform uses distinct permission controls and network frameworks. Below is guidance tailored for the most common device types.
Windows 10 / Windows 11
Ensure all required networking services are active, including Remote Access Connection Manager, which is responsible for VPN tunnel management. If IPv6 is enabled on a network where routing is not properly configured, temporarily disabling IPv6 can prevent tunneling conflicts.
Updating Wi-Fi or Ethernet drivers may resolve authentication failures that occur when outdated drivers block secure connection setup. When issues appear to originate from hardware or adapter configuration rather than Norton itself, the built-in Network Troubleshooter can help identify the source.

macOS
Norton requires approval of system extensions under Privacy & Security settings. If those extensions were blocked during installation, the VPN may fail without displaying detailed errors. After macOS upgrades, older VPN profiles sometimes remain and conflict with the current installation. Removing outdated entries in Network settings and reauthorizing the active configuration can restore connectivity.
iPhone and iPad
iOS may retain expired or duplicate VPN configuration profiles. Removing unused Norton configurations ensures the system uses only the correct one. Features such as Low Data Mode and Low Power Mode can interrupt background processes required for VPN handshakes. Additionally, public networks with captive portals require the user to complete authentication screens before VPN traffic is permitted.
Android
Some Android devices restrict background processes, which may interrupt the VPN tunnel. Allowing background data for the Norton app helps maintain a stable connection. If the VPN repeatedly gets stuck while connecting, clearing the app’s cache and stored configuration data can eliminate corrupted files. While “Always-on VPN” offers enhanced enforcement, enabling it can cause connection failures on networks that are not fully compatible.
Understanding how each platform handles VPN permissions and network routing can make troubleshooting more efficient and reduce unnecessary steps.
Norton VPN Error Situations and Their Meaning
Users often encounter unhelpful error screens without understanding what caused them. A clearer interpretation offers practical direction.
If Norton VPN displays messages indicating no internet connection, the local network is the primary issue and internal fixes will not help until connectivity is restored. When the VPN appears stuck on “connecting,” a conflicting firewall or overlapping VPN installation is the usual cause. If the VPN toggle is disabled or greyed out, subscription or login problems should be addressed first.
Errors appear random to users but typically reflect logical security or network rule enforcement. Identifying the reason behind an error message is essential for efficiently selecting the correct solution.
When Norton VPN Cannot Be Fixed on the Current Network
Even with complete troubleshooting, Norton Secure VPN may continue to struggle if the network environment restricts VPN signals. Public Wi-Fi and business-managed networks frequently block encrypted traffic or limit access to VPN servers. Users who must rely on these networks regularly may find persistent issues unavoidable regardless of device changes.
In these cases, switching to a different VPN provider may be the most efficient path to secure browsing. The root cause is not that Norton is incapable of encryption but that its infrastructure and tunneling flexibility are less robust than dedicated VPN services designed for wider compatibility and consistent performance on restrictive networks.
Objective Comparison: Norton Secure VPN vs. BearVPN
When Norton VPN continues to experience connectivity or performance issues, it can be helpful to compare it with a dedicated VPN service. Norton Secure VPN is designed as part of an all-in-one security suite, which provides basic protection but may lack the flexibility and infrastructure needed for consistent performance in more demanding scenarios.
BearVPN is a standalone VPN service built specifically to deliver stable and secure encrypted connections across different network environments. Because it focuses solely on VPN capabilities rather than being bundled with antivirus software, it maintains more consistent performance and reliability. Its key advantages include:
- Purpose-built VPN service designed for stable, encrypted access
- Strict no-logs policy to maximize user privacy
- Wider global server coverage with faster connection speeds
- Strong compatibility with public or restricted networks
- Lower system resource usage for smoother device performance
While Norton Secure VPN offers encryption, it retains certain identifiable user and session data as part of its logging policy. Users who prioritize anonymity may therefore prefer a no-logs service like BearVPN, which does not collect or store connection or activity information.
Device coverage also differs. Norton limits simultaneous device connections depending on the product tier, whereas BearVPN includes multi-device support by default with fewer configuration restrictions.
If troubleshooting does not resolve Norton VPN reliability issues, switching to a dedicated VPN like BearVPN can provide a more dependable long-term solution for secure browsing, streaming access, and consistent use on a wide variety of networks.
Final Assessment and Recommendations
In most cases, Norton VPN issues can be resolved by following the structured troubleshooting steps in this guide. Common causes include network instability, outdated software, firewall restrictions, or conflicting configurations. Once these problems are corrected, the VPN generally returns to normal operation.
However, Norton Secure VPN is built primarily as a basic security feature within Norton 360. Users who require stable performance on public Wi-Fi, frequent travel, or access to geo-restricted content may find its capabilities limited.
If instability continues after thorough troubleshooting, a dedicated VPN service such as BearVPN may be a more reliable long-term solution. BearVPN offers stronger global performance, a no-logs privacy approach, and broader compatibility across different network environments.
The priority is maintaining secure and private internet access. Whether that is achieved by successfully restoring Norton VPN or choosing an alternative solution depends on your specific needs and usage conditions. This guide provides the information needed to make the most suitable choice.